80 Knee Anatomy Venous
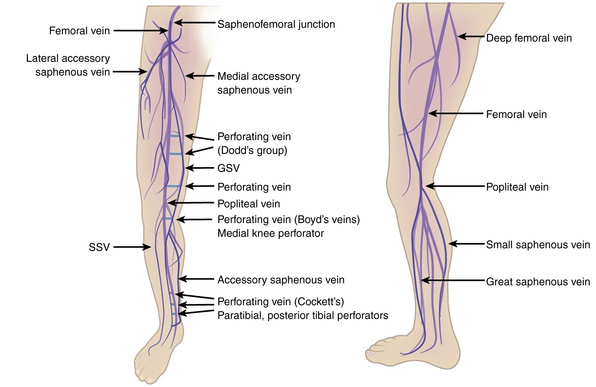
The superficial venous system includes the great saphenous vein GSV the small formerly short or lesser saphenous vein SSV and their numerous tributaries. Normal Resting Supine Venous Pressure in the foot is approximately 80 - 100 mmHg.
We distinguish between the superficial and the deep venous systems.

80 knee anatomy venous. Each anatomical structure is labelled interactively. 5 The lateral plantar artery. 4 Approximately 60 of small saphenous veins join the popliteal vein within 8 cm of the knee joint 20 join the great saphenous vein.
At the back of the knee the popliteal artery lies deep to the nerve and to the popliteal vein. 9 10 At rest arterial inflow is balanced by the action of the respiratory pump and pressure in the deep and superficial veins is equal. As the vein moves up the leg it receives tributaries from other small superficial veins.
If the popliteal vein is also damaged after knee dislocation venous repair is required and can be accomplished by lateral repair or interposition vein grafts. The superficial venous system which resides in the superficial tissue compartment between the deep muscular fascia and the skin. The knee joint is a hinge type synovial joint which mainly allows for flexion and extension and a small degree of medial and lateral rotation.
The superficial system and the deep system1. Anatomy of the venous system. Veins in the lower ext originate at the.
The deep veins accompany the arteries below the fascia and muscles. The deep system which parallels the tibia and femur. The venous system in the lower extremities can be divided for purposes of understanding into three systems.
Venous leg ulcers VLUs are defined as open lesions between the knee and ankle joint that occur in the presence of venous disease1 They are the most common cause of leg ulcers accounting for 60-80 of them2 The prevalence of VLUs is between 018 and 13 Over the age of 65 the prevalence increases to 44. The deep veins of the thigh begin distally with the popliteal vein as it courses proximally behind the knee and then passes through the adductor canal at which point its name changes to the. To see the artery better well go to a different dissection in which the muscles are intact and the nerve and the vein have been removed.
O The lateral plantar vein length between 80 mm 5 and 84 mm 6 is curved constantly doubled and large 2 mm with fusiform dilatations resembling the gastrocnemius sinuses 3 and it is located between the two muscle layers of the sole of the foot ie quadratus plantae and abductor allucis. The superficial MCL also known as a tibial collateral ligament or vertical component of the MCL is part of the middle layer of the medial capsuloligamentous complex of the knee. And the perforating or connecting veins which join the superficial to the deep systems.
Its proximal attachment is the posterosuperior aspect of the medial femoral epicondyle anteroinferior. Written By Unknown Monday July 8 2019 Add Comment. Proximally directed valves are present in the lateral plantar vein.
The immediate post-AVP is about 20 of the resting supine venous pressure. 4 5 The GSV begins anterior to the medial malleolus. The principal deep venous trunk of the leg is called the popliteal vein PV from below the knee until it passes upward and anteriorly through the adductor canal in the distal thigh where it is called the femoral vein FV for the remainder of its course in the thigh.
Concomitant veins - refers to a vein that is usually paired with a vein lying on either side of a single artery Radial ulnar PTV ATV peroneal and gastrocnemius veins are example of concomitant veins. The sinuses and the veins both drain deoxygenated blood from the surfaces of the brains hemispheres2. Deep digital veins- metatarsal veins- PTVs and peroneal veins- tibioperoneal trunk- ATVs- popliteal vein- superficial femoral vein- common femoral vein- external iliac vein.
Anatomy of the knee mri atlas of the human body using cross sectional imaging. The type of PAGSVL joining to the great saphenous vein GSV was above the knee level in 4 4 limbs at the knee level in 14 14 limbs and below the knee level in 74 of patients 74 limbs. Resting venous pressure in the upright position rises by approximately 08 mm Hg per centimeter below the right atrium and reaches 80 to 100 mm Hg at the ankle varying with height weight and calf muscle volume.
13 The sural nerve ascends immediately lateral to the vein which usually lies on and then beneath the muscular fascia prior to its termination. In this article we shall examine the anatomy of the knee joint its articulating surfaces ligaments and neurovascular supply. Knee Anatomy Venous.
Pedal Venous Anatomy The venous drainage of the foot follows a deep system and a superficial system. The superficial veins are located in the subcutaneous tissues superficial to the main muscle fascia. The anatomy of the knee knee bones knee muscles knee arteries knee veins and nerves looking into the.
The superficial cerebral system has sagittal sinuses and cortical veins. 80 of the blood in the body is found in the venous system. The small saphenous vein usually has 7 to 10 closely spaced valves.
The venous system is that part of the circulation in which the blood is transported from the periphery back to the heart. Three below and two above the knee. In simpler words the great saphenous vein starts at an inch away from the large toes and runs along the leg upwards along the calves through the side of the knee onto the anterior side of the thighs and into saphenous opening.
The superficial subcutaneous venous system in the legs includes the long saphenous vein and the short saphenous vein. A little above the knee the popliteal vessels are joined by the sciatic nerve. The relationship between posterior tibial perforators and PAGSVL was seen in 303 of cases 3 limbs.
Fasciotomy is required in the treatment of 50 to 80 of patients with injury to the popliteal artery and is associated with a significant. It ascends up the medial side of the leg passing anteriorly to the medial malleolus at the ankle and posteriorly to the medial condyle at the knee. It is formed by articulations between the patella femur and tibia.
Confluence of SMV and splenic vein. Deep venous insufficiency may result from increased pressure from superficial insufficiency Post phlebitic syndrome may develop pain edema pruritis hypohydrosis eczema and eventually ulceration Venous Claudication may occur deep incompetency and. Valves are numerous in the deep venous system but are also present in the superfi-.
In venous anatomy the great saphenous vein is a superficial subcutaneous vein. Anatomy of the popliteal artery. With calf-muscle contraction blood is forced up the deep veins Foot Pump also contributes.
Although historically called the superficial femoral. Flow of lower ext deep veins. The MCL measures 8-10 cm in length and has superficial and deep portions 4.
The intracranial or cerebral venous system is a network of nerves made up of two systems working together. Venous Pathophysiology Chronic Venous Insufficiency is caused by either impaired venous. Anatomy of the knee mri atlas of the human body using cross sectional imaging.
The vessel ascends along the medial aspect of the calf and thigh superficial to the muscular fascia It then passes through the saphenous opening of the deep fascia and enters.

Venous Drainage Of Leg Anatomy Popliteal Artery And Vein Small Saphenous Vein Plantaris Muscle And Tendon Plan In 2021 Leg Anatomy Human Body Muscles Body Anatomy

References In Multi Disciplinary Quality Improvement Guidelines For The Treatment Of Lower Extremity Superficial Venous Insufficiency With Ambulatory Phlebectomy From The Society Of Interventional Radiology Cardiovascular Interventional Radiological
History Of Venous Surgery 1 Servier Phlebolymphologyservier Phlebolymphology

Anatomy Of The Lower Limb Venous System And Assessment Of Venous Insufficiency Radiology Key Venous Insufficiency Lower Limb Vascular Ultrasound

Venous Anatomy Physiology And Pathophysiology Sciencedirect

Sclerotherapy Basicmedical Key
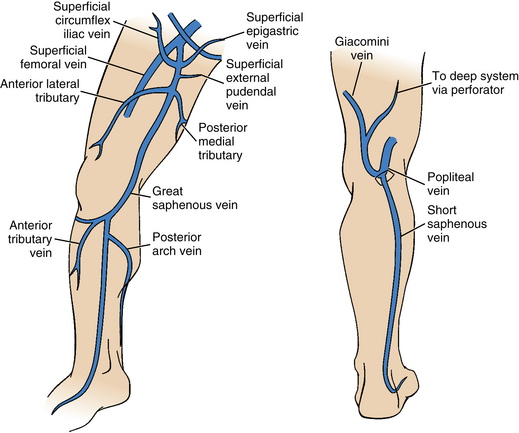
Lower Extremity Veins Radiology Key

Venous Segments Used To Assess Thrombus Extension Civ Common Iliac Download Scientific Diagram

Buerger Allen Exercises 8abs Com Natural Cure For Arthritis Arthritis Remedies Healthy Legs
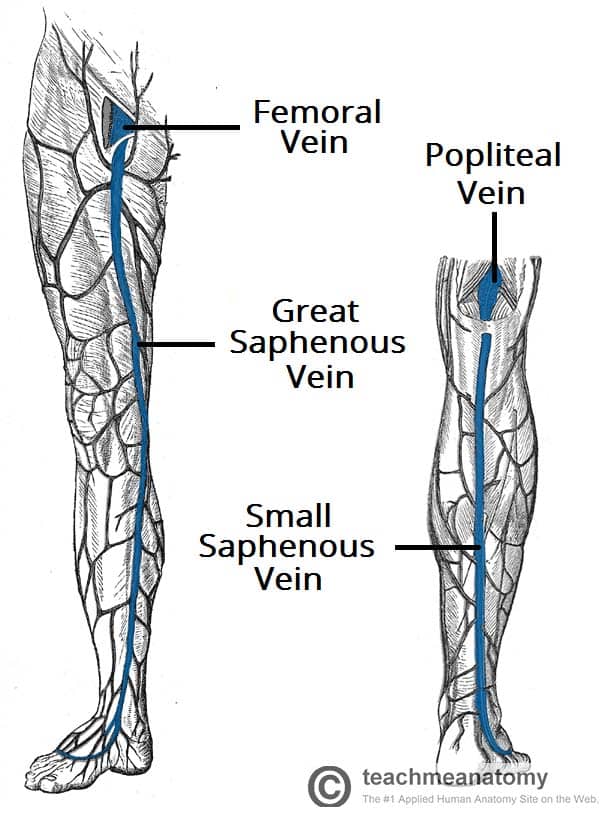
Blood Vessels And Lymphatics Of The Lower Limb Teachmeanatomy

Pelvic Arteries Arteries Anatomy Human Body Anatomy Muscle Anatomy

Venous Anatomy Physiology And Pathophysiology Sciencedirect